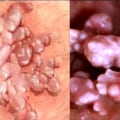
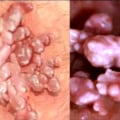
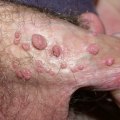
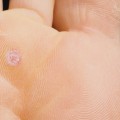
Genital warts are a common sexually transmitted infection (STI) caused by certain strains of human papillomavirus (HPV). They usually appear as bumpy cauliflower-like growths, but some may be flat. Genital warts don't usually cause pain or discomfort, but they can itch, bleed, or make sexual intercourse painful. The goals of treating genital warts are to remove the warts and reduce any symptoms.
In women, genital warts appear in and around the vagina or anus, or on the cervix. They can be very small or appear as large groups. They can be reddish or white in color. Sometimes, you may have genital warts but not show any symptoms.
Genital warts won't bleed if a person doesn't alter them. However, friction when walking or having sex can irritate or tear warts. Warts can break open, bleed, or become infected because of friction or if they get caught on something. Even when there are no genital warts, HPV can be present on the skin and spread during sexual contact.
The type of treatment for warts depends on many factors, such as the size, shape, location, cost, and preferences of the patient and health care provider. The doctor will examine you or take a biopsy (a sample of the wart) to see if you have genital warts. People with genital warts should assume that they are contagious and discuss risk and risk mitigation strategies with their partners. Two strains of HPV, in particular HPV 6 and HPV 11, are responsible for approximately 9 out of 10 cases of genital warts.
Having genital warts can cause feelings of anxiety, depression and a sense of diminished quality of life, especially at the time of first diagnosis. Genital warts are also known by other names, such as genitoanal warts, anogenital warts, or condyloma acuminata. The doctor may recommend having a regular Pap smear or other tests depending on the person's history of genital warts. For this reason, the fact that a person has not had sexual contact recently does not exclude the possibility of having genital warts.
Sometimes genital warts go away on their own when left untreated, while other times they stay the same or even increase in number and size. Genital warts can be a source of distress for many people due to their appearance and potential to cause discomfort during sexual intercourse. It is important to understand how to identify them and what treatments are available to help manage them.
What Causes Genital Warts?
Genital warts are caused by certain strains of human papillomavirus (HPV). HPV is a virus that is spread through skin-to-skin contact during sexual activity.It is estimated that up to 75% of sexually active adults will have been exposed to HPV at some point in their lives.
How Are Genital Warts Diagnosed?
The doctor will examine you or take a biopsy (a sample of the wart) to see if you have genital warts. It is important to note that even if you do not have visible signs of genital warts, it does not mean that you do not have HPV. A Pap smear may be recommended if there is any suspicion that you may have been exposed to HPV.What Are The Treatment Options For Genital Warts?
The type of treatment for genital warts depends on many factors such as size, shape, location, cost and preferences of the patient and health care provider. Treatment options include topical creams and ointments applied directly to the wart; cryotherapy which involves freezing off the wart; laser therapy which uses heat energy to destroy the wart; surgical removal; and electrocautery which uses an electric current to burn off the wart.Can Genital Warts Go Away On Their Own?
Sometimes genital warts go away on their own when left untreated while other times they stay the same or even increase in number and size.It is important to note that even if the visible signs of genital warts go away it does not mean that the virus has been eliminated from your body.