If you're looking to treat genital warts, it's best to consult a dermatologist. Over-the-counter wart medications are not suitable for treating genital warts, as they are designed to treat other types of warts. However, some creams may be able to boost the immune system's ability to fight genital warts. It's important to avoid sexual contact while the cream is on the skin, as it can weaken condoms and diaphragms, and irritate your partner's skin.
During an office visit, a dermatologist will examine the warts and may take a sample for laboratory testing to confirm the diagnosis. Although some genital warts may go away without treatment, seeing a dermatologist can provide peace of mind and quicker removal. In some cases, the body's immune system is able to fight off the virus naturally, meaning that no signs or symptoms of genital warts will develop. Genital warts can disappear on their own, but they may also enlarge or multiply.
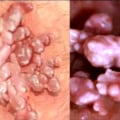
It's important to note that the types of HPV that cause genital warts are different from those that can cause cancer. Genital warts have a 'cauliflower-like' appearance, rather than being smooth. Some people infected with HPV don't know they carry the virus as they never develop genital warts. Women should have regular pelvic exams and Pap tests to detect any vaginal or cervical changes caused by genital warts or early signs of cervical cancer.
If you haven't seen your doctor yet, you may be wondering if you have genital warts and how to get rid of them. Treatment options vary depending on the location and size of the warts. Genital warts are more common in women on the external genitalia and in men on the penis, scrotum, and thighs. If genital warts return after treatment, speak to your nurse or doctor about options for removing them again.
It's important to remember that treating genital warts can take months or even years as the human papillomavirus is very good at evading the immune system.