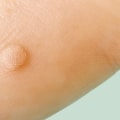
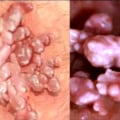
Genital warts are soft bumps on the skin and mucous membranes of the genitals that can be found on the penis, vulva, urethra, vagina, cervix, and around and inside the anus. They look like little pieces of cauliflower, may be big or small, and may itch but usually don't hurt. To confirm if you have genital warts, a doctor will examine you or take a biopsy (a sample of the wart). Depending on the results, they may also refer you to a specialist for further tests.
A blood sample may also be taken to test for HIV and syphilis. Genital warts are usually diagnosed visually, although a biopsy may be needed to confirm it. Small warts can sometimes be confused with mollusc contagious. Genital warts usually rise above the surface of the skin, present parakeratosis and present nuclear changes typical of HPV infections (nuclear enlargement with perinuclear elimination). DNA testing should not be used for diagnosis or for low-risk HPV infections. It can take several weeks, months, or even years after having sexual contact with someone who has genital warts for them to appear.
For women, it's important to have regular pelvic exams and Pap tests, which can help detect vaginal and cervical changes caused by genital warts or the early signs of cervical cancer. If you have genital warts, a healthcare provider should examine all of your sexual partners and treat them if warts are found. If you have warts or red bumps on or around your genitals, if your partner has HPV or another STD, or your partner has genital warts, see your doctor or nurse or contact your local Planned Parenthood health center. A large number of cases of genital warts do not respond to treatment and often recur, especially with repeated infections caused by sexual contact or by the long incubation period of HPV. Be sure to get screened for cancer of the cervix, vagina, vulva, or anus if you have been diagnosed with genital warts. Genital warts are caused by low-risk types of human papillomavirus (HPV). Types 16 and 18 cause approximately 70% of cervical cancers, and types 6 and 11 cause approximately 90% of genital warts.
Symptoms of genital warts caused by HPV in men include small bumps or groups of bumps on the tip or shaft of the penis, scrotum, or anus.